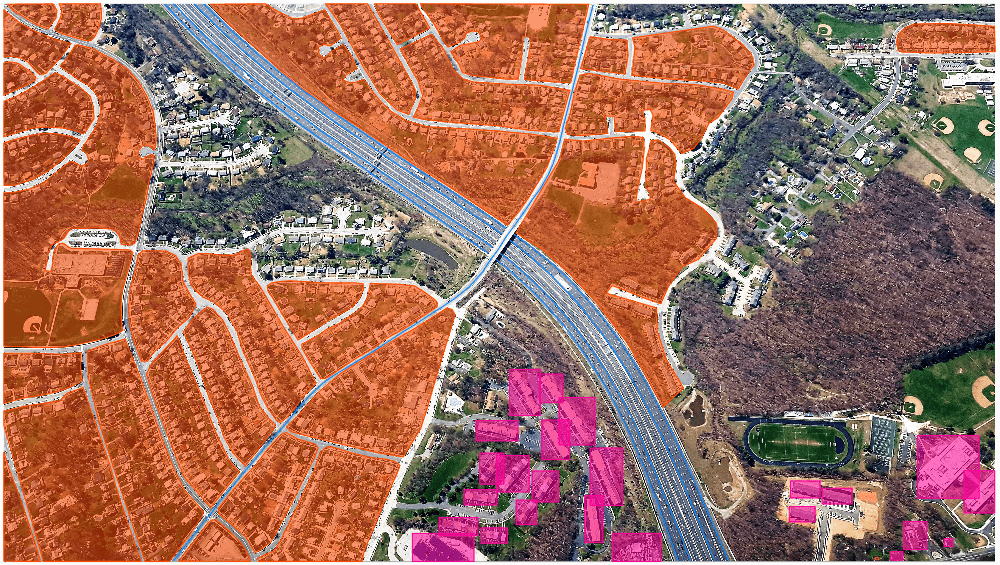
Geospatial data annotation, a term gaining prominence in today’s tech-driven world, refers to the process of labeling or tagging geographical information within datasets. This practice has become indispensable across various industries, shaping the way machines interpret and navigate the world around us.
Applications of Geospatial Data Annotation
Autonomous Vehicles
One of the primary applications of geospatial data annotation is in the realm of autonomous vehicles. Accurate annotation allows these vehicles to understand and respond to their surroundings, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
Satellite Imagery Analysis
In satellite imagery analysis, geospatial data annotation plays a crucial role in identifying and categorizing geographical features. This aids in tasks such as environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster response.
Augmented Reality
Geospatial data annotation contributes significantly to the immersive experiences offered by augmented reality applications. Precise annotations enable virtual objects to seamlessly integrate with the real-world environment.
Challenges in Geospatial Data Annotation
Despite its importance, geospatial data annotation comes with its set of challenges. Ensuring accuracy in annotations, scalability of annotation processes, and maintaining quality control are critical issues that need attention.
Accuracy Concerns
Achieving high precision in geospatial data annotation is essential, especially in applications like autonomous vehicles, where inaccuracies can lead to severe consequences.
Scalability Issues
As the demand for annotated data grows, scalability becomes a challenge. Efficient systems and processes must be in place to handle large datasets within reasonable timeframes.
Quality Control
Maintaining the quality of annotations requires robust quality control measures. Regular audits, feedback loops, and continuous improvement strategies are vital components of a successful annotation process.
Tools and Technologies
Advancements in artificial intelligence have paved the way for sophisticated tools and technologies in geospatial data annotation.
AI-Powered Annotation Tools These tools leverage machine learning algorithms to automate the annotation process, significantly reducing the time and effort required.
Machine Learning Algorithms Machine learning algorithms play a pivotal role in automating the annotation of geospatial data. They learn from existing annotations and improve over time, enhancing the overall efficiency of the process.
Human-in-the-Loop Systems While automation is valuable, human expertise remains crucial, especially in complex scenarios where machine algorithms may fall short. Human-in-the-loop systems ensure a nuanced understanding of the data.
Benefits of Accurate Geospatial Data Annotation
Enhanced Machine Learning Models
Accurate annotations contribute to the development of robust machine learning models. These models, trained on precisely annotated data, exhibit higher accuracy in various applications.
Improved Navigation for Autonomous Vehicles
In the context of autonomous vehicles, accurate geospatial data annotation is paramount for precise navigation. It enables vehicles to interpret and respond to dynamic road conditions effectively.
Precision in Geospatial Analysis
For applications such as urban planning and environmental monitoring, precise geospatial data annotation ensures reliable and insightful analysis, leading to informed decision-making.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Agriculture
In agriculture, geospatial data annotation aids in crop monitoring, yield prediction, and resource optimization, contributing to sustainable and efficient farming practices.
Urban Planning
Urban planners use annotated geospatial data to analyze and design cities more effectively, considering factors like traffic patterns, infrastructure development, and environmental impact.
Emergency Response Systems
In emergency response systems, accurate annotations facilitate rapid and effective decision-making during crises, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies.
The Role of Human Annotation in Geospatial Data
While automation is advancing, human annotation remains invaluable in certain scenarios.
Human Expertise in Complex Scenarios
Humans bring contextual understanding and adaptability to complex scenarios, ensuring accurate annotation in situations where automated systems may struggle.
Ensuring Nuanced Understanding
In cases where interpretation requires a deeper understanding of cultural or contextual nuances, human annotators play a crucial role in providing accurate annotations.
Future Trends in Geospatial Data Annotation
The field of geospatial data annotation is evolving rapidly, with several exciting trends shaping its future.
Integration with 5G Technology
The integration of geospatial data annotation with 5G technology is expected to enhance real-time processing capabilities, enabling quicker and more efficient annotation processes.
Advancements in Machine Learning
Continuous advancements in machine learning algorithms will further improve the accuracy and efficiency of geospatial data annotation, expanding its applications.
Quality Control Measures
To ensure the reliability of annotated geospatial data, robust quality control measures must be in place.
Regular Audits Regular audits of annotated datasets help identify and rectify errors, ensuring the ongoing accuracy of the data.
Feedback Loops Establishing feedback loops between annotators and quality control teams facilitates continuous improvement and learning from mistakes.
Continuous Improvement Strategies Adopting strategies for continuous improvement ensures that the geospatial data annotation process evolves with changing requirements and challenges.
Ethical Considerations in Geospatial Data Annotation
As geospatial data annotation becomes more prevalent, ethical considerations come to the forefront.
Privacy Concerns
Annotation of geospatial data often involves information about individuals and their locations. Striking a balance between data utility and privacy protection is crucial.
Bias in Annotation
Care must be taken to address biases in annotation, as it can impact the accuracy and fairness of machine learning models trained on annotated data.
Training and Skill Development
The effectiveness of geospatial data annotation relies on the skills of annotators and the continuous development of their expertise.
Importance of Skilled Annotators
Skilled annotators bring precision and understanding to the annotation process, ensuring high-quality annotated datasets.
Training Programs and Certifications
Establishing training programs and certifications for geospatial data annotators contributes to the professionalization of this field, enhancing the overall quality of annotations.
Global Impact of Geospatial Data Annotation
The widespread adoption of geospatial data annotation has significant global implications.
Economic Benefits
Industries leveraging accurately annotated geospatial data experience economic benefits through improved efficiency, informed decision-making, and the development of innovative solutions.
Environmental Impact
In fields like agriculture and environmental monitoring, the impact of geospatial data annotation extends to sustainable practices, resource optimization, and mitigating environmental risks.
Comparative Analysis of Annotation Methods
Manual Annotation vs Automated Methods
A balanced approach that combines the strengths of manual annotation and automated methods often yields the best results, addressing the limitations of each approach.
Hybrid Approaches
Hybrid annotation approaches, integrating human expertise with machine efficiency, offer a pragmatic solution to complex geospatial data annotation requirements.
Collaboration in Geospatial Data Annotation
Collaboration among industries, researchers, and annotators is essential for advancing the field.
Industry Partnerships
Collaborations between technology companies, research institutions, and industries ensure the development of cutting-edge tools and methodologies for geospatial data annotation.
Crowdsourcing Efforts
Engaging the global community through crowdsourcing efforts can accelerate the annotation process, leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, geospatial data annotation plays a pivotal role in transforming how machines perceive and interact with the world. From autonomous vehicles to urban planning, its applications are vast and diverse. The future promises exciting advancements with the integration of 5G technology and continuous improvements in machine learning algorithms. However, ethical considerations, quality control, and collaboration remain crucial for the responsible and effective implementation of geospatial data annotation.
FAQs
- What is geospatial data annotation? Geospatial data annotation involves labeling or tagging geographical information within datasets, enabling machines to understand and interpret location-based data.
- Why is accuracy crucial in geospatial data annotation? High accuracy ensures that machine learning models trained on annotated data make precise decisions, especially in applications like autonomous vehicles.
- How can biases in geospatial data annotation be addressed? Addressing biases involves implementing diverse and inclusive annotation processes, considering cultural and contextual nuances, and regular audits to identify and rectify biases.
- What is the role of human annotation in the age of automation? Human annotation remains essential, especially in complex scenarios where contextual understanding and adaptability are crucial for accurate annotations.
- How can industries benefit from geospatial data annotation? Industries can experience economic benefits, improved efficiency, and informed decision-making by leveraging accurately annotated geospatial data for various applications.