Many IT companies have recently taken up data warehouse development. This service has become very popular among various business owners. What is the purpose of a data warehouse? First, this technique helps to significantly reduce the cost of storing and protecting commercial information. Second, this solution speeds up and improves end-to-end data analytics. Thirdly, reports can be received at any time and control the activities of the company in real time. Fourth, it becomes easy to set up access levels for employees from different departments. Since many people still do not know what the difference between database and data warehouse is, we wrote this article.
Database features
This type of software has the following functions:
- Stores information about one part of the company’s workflow;
- Handles daily transactions (for example, the sale of goods);
- Quickly handles simple user requests.
Warehouse Distinctive features
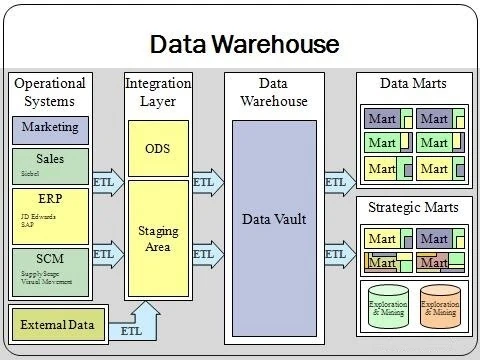
Is a data warehouse a database? No. In this case, we are talking about a system that collects data from custom sources. The software automatically analyzes and sorts information. This data is then made available for monitoring and reporting. These reports allow you to make informed decisions and plan a strategy for further business development. Read more about Data Warehouse Concepts here: https://blog.dataart.com/data-warehouse-concepts-and-tools-do-s-and-don-ts-while-building-your-solution.
A Guide to Criteria for Differences Between the Two Kinds of Software
The main difference lies in the use of different types of data processing:
- Databases use online transaction processing (OLTP). This is necessary to quickly update (add, delete or replace) a large volume of current operations. Transactions are made almost instantly. Online ticket booking is a classic example of such a protocol.
- Cloud storage uses online analytical processing (OLAP). This helps to quickly analyze and sort a huge amount of constantly arriving new information. For example, such a protocol allows you to instantly summarize daily receipts in the form of a daily report.
In other words, databases are optimized to respond quickly to many simple queries. Repositories must perform a small number of complex queries against large amounts of heterogeneous data.
There is also a difference in the structure of the information. Databases subject any data to normalization. The system automatically removes duplicate information. This speeds up the process of processing requests, but complicates the process of analytics. Normalization splits information into multiple tables. If you need to compile a report, then the system takes a long time to analyze all these tables. In data warehouses, complex multidimensional queries are processed almost instantly.
What else do you need to know?
The main differences depend on the specific properties inherent in each type of software:
- The structure of the data in the repositories allows you to retrieve information faster, but it is less accurate. Databases provide access to large amounts of information very slowly, but it will be more accurate.
- The chronology of the data for the databases is the current information about one area of the business, which appears instantly. The data chronology for the warehouse is a summary of all areas of the company for the entire period of its existence.
- Only one user can make changes to the database in real time. Several users can work with the storage data simultaneously.